©Carole Tyrrell
Today it is Candlemas, an important day in the church calendar. It takes place 40 days after Christmas and marks the end of the Christmas period. A Christian feast day, it celebrates the presentation of Jesus at the Temple and the purification of Mary. But it is also associated with another significant event – the appearance of snowdrops in churchyards and cemeteries with their tiny nodding white heads in the breeze. A sign that Spring is on its way.
It’s always at this time of year that I repeat this post. For these delicate little flowers have another darker side to them and a long association with churchyards and death.
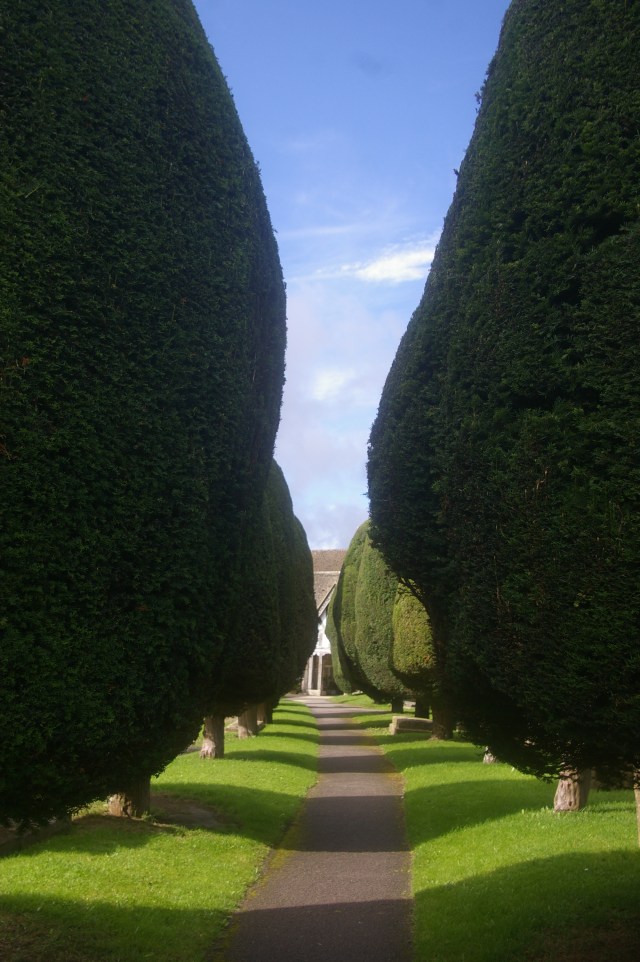
Imagine yourself in a gloomy medieval church on the festival of Candlemas. You, and your fellow parishioners, have each brought your candles to be blessed by the priest and, after the procession which will fill the church with light, they will all be placed in front of a statue of the Virgin Mary. Candlemas marked the end of winter and the beginning of Spring and the blessing is to ward off evil spirits. It traditionally falls on February 2 and is shared with the Celtic festival of Imbolc. And in the churchyard outside you can see green shoots forcing their way up through the hard winter earth as the snowdrop’s milk-white flowers begin to emerge into the light.
The placing of the lit candles in front of the Virgin Mary’s statue gave the snowdrop one of its many other names – Mary’s Tapers. But there are many others such: Dingle Dangle, Candlemas Bells, Fair Maids of February, Snow Piercer, Death’s Flower and Corpse Flower.
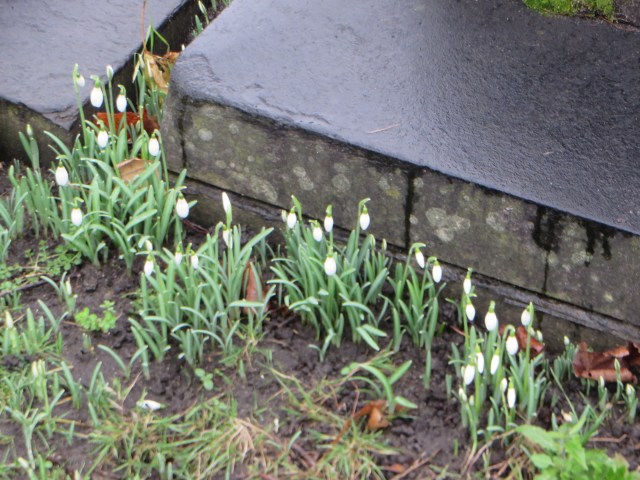

©Carole Tyrrell
The snowdrop’s appearance has also inspired many comments . According to the Scottish Wildlife Trusts website they have been described as resembling 3 drops of milk hanging from a stem and they are also associated with the ear drop which is an old fashioned ear ring. Anyone who has seen a group of snowdrops nodding in the wind will understand what they mean. The snowdrop’s colour is associated with purity and they have been described as a shy flower with their drooping flowers. However, the eco enchantments website reveals that the flower is designed in this way due:
‘to the necessity of their dusty pollen being kept dry and sweet in order to attract the few insects flying in winter.’
Snowdrops have been known since ancient times and, in 1597, appeared in Geralde’s ‘Great Herbal’ where they were called by the less than catchy name of ‘Timely Flowers Bulbous Violets’. Its Latin name is Galanthus nivalis. Galanthus means milk white flowers and the nivalis element translates as snowy according to the great botanist, Linnaeus in 1753. In the language of flowers they’re associated with ‘Hope’, the coming of spring and life reawakening.
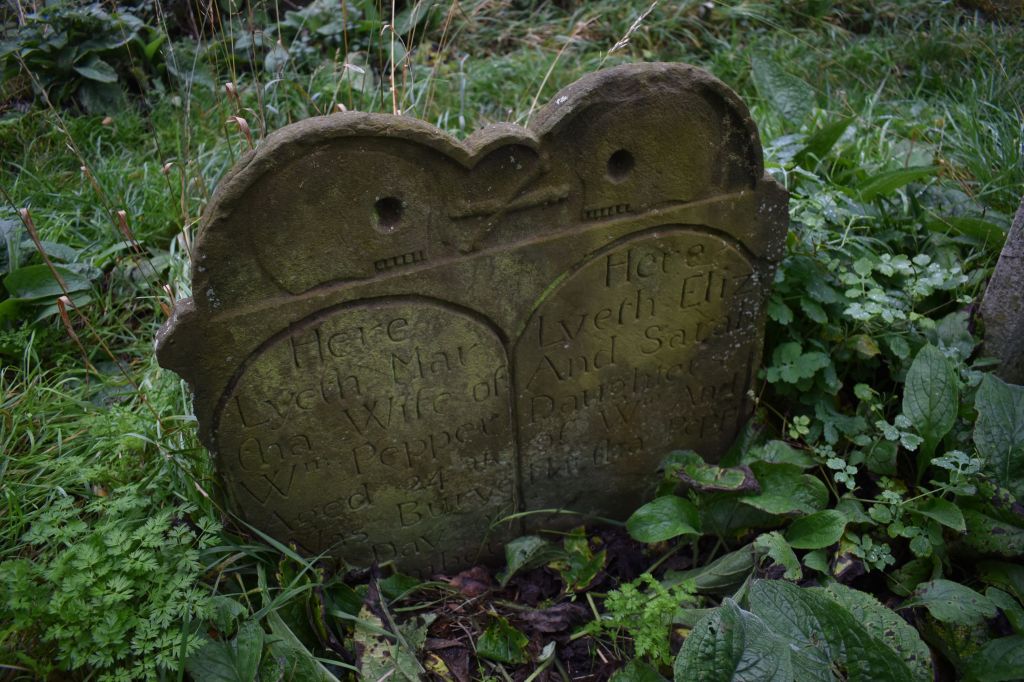
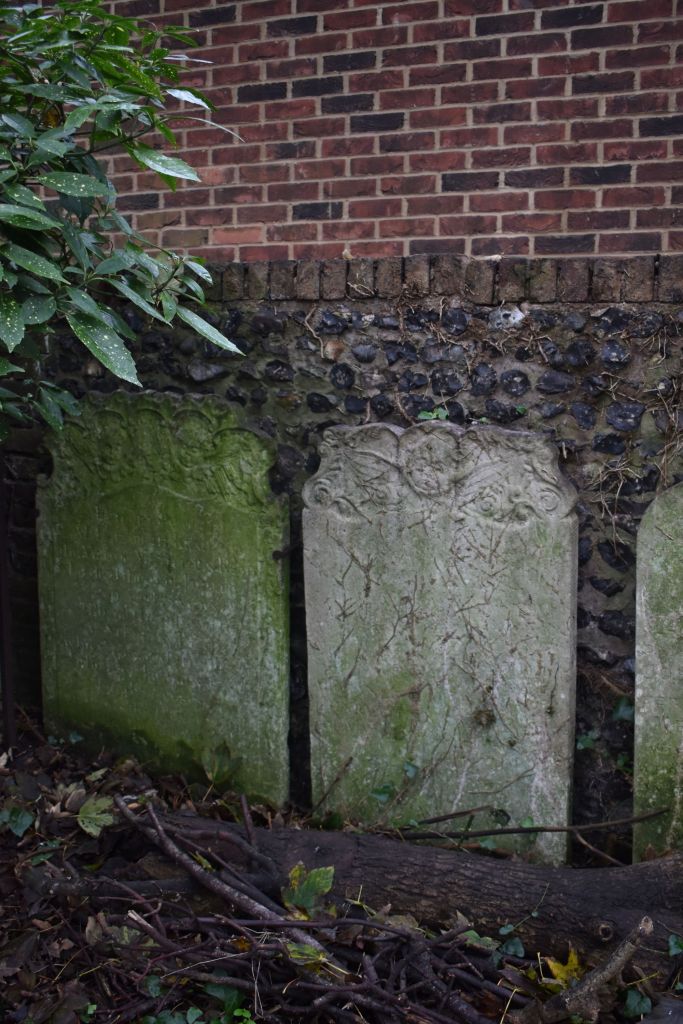
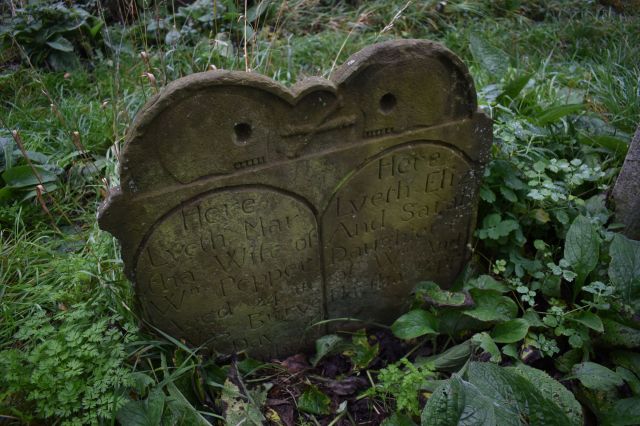
However, yet despite all these positive associations, the elegant snowdrop has a much darker side. Monks were reputed to have brought them to the UK but it was the ever enthusiastic Victorians who copiously planted them in graveyards, churchyards and cemeteries which then linked them with death. Hence the nickname name ‘Death’s Flower.’
They were described by Margaret Baker in the 1903 ‘Encyclopedia of Superstitions, Folklore and the Occult of the World’ as:
‘so much like a corpse in a shroud that in some counties the people will not have it in the house, lest they bring in death.‘
So that’s where the ‘Corpse Flower’ nickname came from.
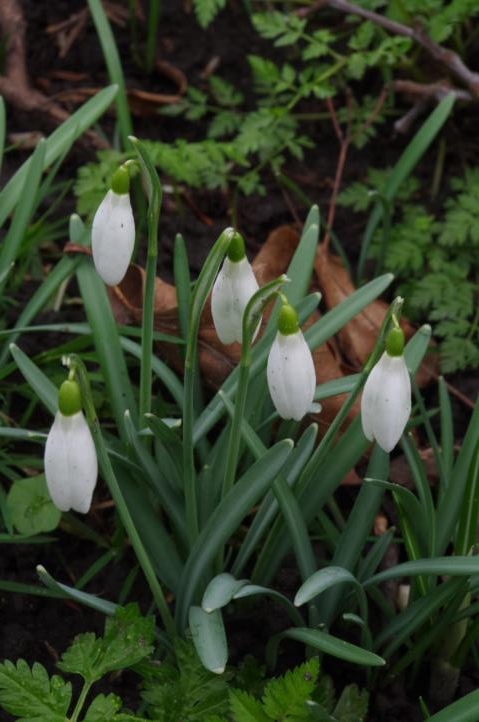

©Carole Tyrrell
Snowdrops are also seen as Death’s Tokens and there are several regional folk traditions of connecting death with them. For example in the 19th and early 20th centuries it was considered very unlucky to bring the flower into the house from outside as it was felt that a death would soon occur. The most unlucky snowdrop was that with a single bloom on its stem. Other folk traditions were described in a 1913 folklore handbook which claims that if a snowdrop was brought indoors it will make the cows milk watery and affect the colour of the butter. Even as late as 1969 in ‘The Folklore of Plants’ it was stated that having a snowdrop indoors could affect the number of eggs that a sitting chicken might hatch. A very powerful plant if these are all to be believed – you have been warned!
It’s amazing that this little flower has so many associations and legends connected with it but I always see it as a harbinger of spring, rebirth and an indication of warmer days to come.
But the snowdrop also has a surprise. This came courtesy of the Urban Countryman page on Facebook – not all social media is time wasting! If you very gently turn over a snowdrop bloom you will find that the underside is even prettier and they also vary depending on the snowdrop variety.
Here is a small selection of snowdrop undersides from my local churchyard and one from Kensal Green cemetery.

©Carole Tyrrell
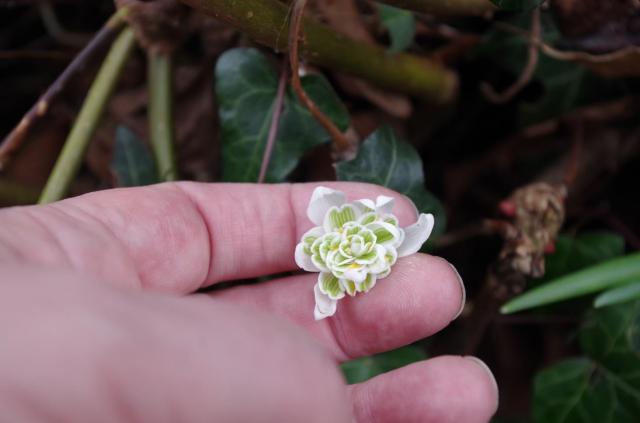

St George’s Beckenham
©Carole Tyrrell

©Carole Tyrrell

©Carole Tyrrell
So don’t underestimate the snowdrop – it’s a plant associated with life and death but watch out for your hens and the colour of your butter if you do decide to tempt fate…..
©Carole Tyrrell text and photos unless otherwise stated
References: